SINUSITIS
Sinusitis , also known as rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the sinuses. There are four types of sinuses (small holes) in the skull known as :
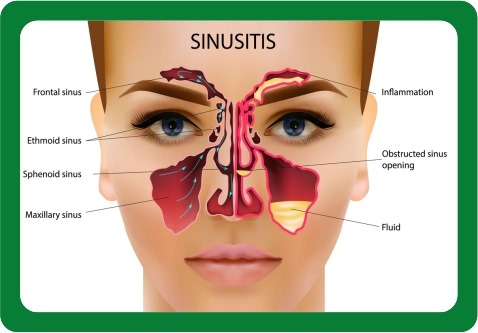
Maxillary Sinus : This is the largest sinus with approximately 15 ml of size in an adult. The maxillary sinus is located on each side of the nose, near the cheekbones. It is a pneumatic cavity in the maxillary bone. It is pyramidal, with a base looking to the nasal cavity, anterior, posterior, and superior walls, and a lateral blunt apex extending into the maxillary bone’s zygomatic process.
Frontal Sinus : The frontal sinus is located above the eyes, near forehead i.e. superior to the orbit and within the frontal bone. It is a highly variable air-filled structure. Its shape and size depend on climate and ethnicity but is more or less pyramidal in adults, and the typical volume is 4 to 7 mL
Sphenoid Sinus : The sphenoid sinus is located behind the eyes, deeper into your skull. between the eyes, on either side of the septum. centrally and posteriorly within the body of the sphenoid bone , and the sella turcica posteriorly and superiorly bounds it. The sphenoid sinus, can be identified in radiographs from the age of 2. It keeps developing throughout life but matures in size at around 12 to 14 years of age. The typical adult size is 0.5 to 8 ml.
Ethmoid Sinus : The ethmoid bone is formed by many cells with an intricated structure through which all the paranasal sinuses drain. 3 to 4 ethmoid air cells at birth develop into 5 to 15 paired cells by adulthood with a total volume of 2 to 3 ml. They are located on each side of the bridge of the nose, near eyes. There are three small pairs of the ethmoid sinuses.
Sinuses make mucus, that is drained out through these sinuses. Sinuses are prone to inflammation and bacterial, viral or fungal infection. When they become blocked from secretions or a mass, mucus drainage is interrupted, causing sinusitis. Malignancies of the sinuses are rare. The majority of cancers occur in the maxillary sinus and are more common in men than women. Maxillary sinus malignancies occur between ages 45 and 70, and the most frequent is a sarcoma. Even though metastases are rare, these malignancies are locally invasive and destructive. Diagnosis is delayed in most cases, and the prognosis is poor.
Trigger Factors :
- Inhaling of small hairs (cilia). This may happen having exposure to pets.
- Cold and Allergies.
- Deviated nasal septum, nasal bone spur, nasal polyps.
- Chronic infection
Symptoms :
- pressure and pain in face, nasal congestion, stuffy or runny nose.
- Pressure or pain in teeth , and/ or ear.
- Cough.
- Bad breath or bad taste in the mouth
- Headache.
- Fever.
Types of Sinusitis : Sinusitis can be of the following types :
- Acute : Normally caused due to viral cold and may last not more than four weeks
- Subacute : This may last four to twelve weeks.
- Chronic : Normally caused due to bacterial infection and last twelve or more weeks.
- Recurrent : This comes four or more times in a year and each time last less than two weeks.
Risk factors :
- Allergic Rhinitis (Hay Fever)
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Diseases preventing cilia from proper working
- Large Adenoids
- Changes in altitude (Flying or Scuba diving)
- Smoking
- Weak immune system
- After effects of certain treatments like chemotherapy
- Impaired sinus structures
Comparison between sinusitis, covid-19, common cold or allergy :
All these, more or less have a common symptoms and it may be difficult to find what the patient is exactly suffering from. However, common cold typically builds, peak and slowly disappear within a week. Allergies are associated with sneezing, itchy nose and eyes, congestion, runny nose and postnasal drip in the throat. Sinusitis is associated with pressure or pain on the face, teeth and/or ear. Covid- 19 may have fever and shortness of breath also along with other common symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests : Nasal Endoscopy or rhinoscopy, Imaging tests – C T Scan, MRI, Allergy test, Blood test to find HIV or poor immunity, Ciliary function test, Nasal culture, Nasal Cytology, Sweat Chloride Test for Cystic Fibrosis.
Treatment : Homoeopathic medicines :
- Throbbing pain and a burning sensation, complaints aggravates when exposed to light, noise, movement, and/or after midnight, exertion and excitability with or without nausea and vomiting – Arsenic 30
- Pressure around the eyes, severe pain in the forehead or around the eyes , waves of pain that come and go as it comes. Intolerable exposure to light. Pain worse on jarring, bending, lying flat, or motion of the eyes – Belladonna 30
- For the later stages when the pain is concentrated between the eyes and is worsened by cold or motion; thick nasal discharge with sensitivity of the scalp – Hepar Sulph 30
- pressure and pain at the root of the nose and in the forehead with thick, stringy and yellowish nasal discharge. scalp and facial bones are tender to touch, pain is worse around noon and with cold and motion, when lying down in the darkened room, but improves with warmth and pressure, – Kali Bich 30
- Sneezing along with thick, green, foul-smelling nasal discharge, which may be blood tinged, hoarseness, dry, rough cough due to continuous tickling in the throat, pressing pain in the forehead, cheeks, upper teeth, and ears, nasal congestion, worse with open air, sleeping, eating, drinking, and extreme hot or cold, marked thirst, bad breath, and restlessness – Merc Sol 30
- Alternate stuffy nose and fluent nasal discharge, pressure around the eyes, sore throat, hoarseness, loss of smell or taste. The mucus can also have stains of blood due to the continuous blowing of the nose – Phosphorus 30
- Lethargy, activities such as sitting, stooping, rising from lying down, and eating can aggravate the pain, lying down in a warm room helps in getting relief from headaches, thick, bland, yellow or greenish discharge that is often accompanied by nausea and indigestion; symptoms tend to improve with cool air, pain is usually in the frontal part, persons who are distinctly not thirsty and require tremendous comforting – Pulsatilla 30
- For individuals with chronic congestion accompanied by head pain that tends to be worse in the right eye; this pain is worsened by cold, movement, light, noise, and mental concentration (such as when studying), but relieved by heat and pressure – Silicia 12X
- Allergic reaction and thereby, inflammation of the sinuses, terrible headache, sharp pains on the left side of the face, Exposure to cold or wet weather, warmth, light, noise, and movement aggravates the problems but are relieved by cold compresses or cool water on the face and when the individual is lying down with the head propped up – Spigella – 30
Treatment : Homoeopathic medicines :
- Do not use any nasal decongestants spray.
- Inhale steam 3-4 times a day, each time at least 20 minutes. If possible, add 3-4 drops Eucalyptus Oil in the water for steam.
- Apply warm moist cloth on the face several times a day.
- Inhale pure Bhimseni Camphor several times a day.
- Jal Neti is very useful but while doing it, ensure that entire water is properly expelled out when jal neti is over. To do so, immediately on completing it, do Kapal Bhati 10-12 times.
- Do not eat any mucus forming things such as Rajma, Choley, Chana, Paneer, Lentils (except moong, month & masoor), Potato, Banana, Arbi, Kaddu, Cauliflower, Peas etc.
- Take plenty of citrus fruits/ fresh citrus juice. Fresh lemon juice in hot water with raw honey 3-4 times a day is a must. Also take plenty of hot herbal tea made from Tulsi, Ginger, Mulethi, Banafsha, Cinnamon, Cloves, Black Pepper and Cardamon . Alternatively, can take our Saumya Herbal Tea.
- Do not take any cold drink, aerated drink , wine , and smoke. Also avoid junk food. Take simple, easily digestible vegetarian food comprising of green vegetables, leafy vegetables, seasonal fruits and sprouted grains.